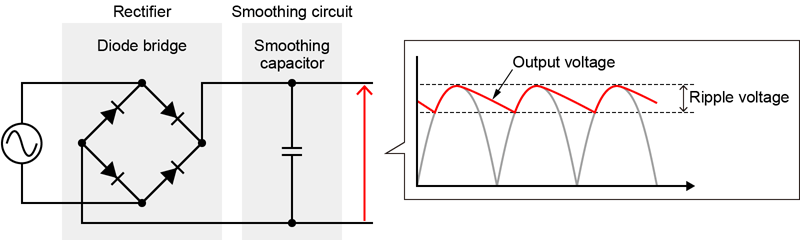
Ripple contributes to constantly varying DC output voltages that produce pulsating content.
The ripple voltage fluctuation synchronizes with the switching frequency, producing an output voltage with superposition characteristics on the output voltage.
The capacitance of the input smoothing capacitor inside the power supply unit, the response speed of the amplifier, the switching frequency, the output filter, and the output current will determine the conditions of the pulsation components.
According to Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA) standard, ripple is defined as fluctuations consisting of frequency components at 50/60Hz, the same as AC power. In contrast to the ripple, noise is defined as fluctuations comprised of frequency components of several tens of kHz or higher caused by AC adapter switching.
Some ripple and noise component are contained on the output. When you need to stabilize the output voltage, using a power supply with low ripple noise is preferable.
Information on related articles in Technical Knowledge
- What is a Power Supply? Types and Applications
- What is a Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supply
- What is DC power supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- What is a Bipolar Power Supply? (Basic Knowledge)
- Fundamentals of Electronic Loads: Types, Principles, Usage, and Configuration
- What is an AC Power Source (Basic Knowledge)
- Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies: Key Differences Explained
- Types of X-ray tubes and high-voltage power supplies
- High Voltage Measurement Method
- How to choose the DC power supply? Explanation of the points.
- Difference between DC power and AC power
- For New Electronics Engineers, How to Use the Power Supply Safely
- Installation of DC Power Supply and remote sensing correctly and safely
- How to Select a High Voltage Power Supply for Laboratory Analyzers
- Basics of amplifiers, how to use the amplifier and precautions
- Method of Generating Direct Current (DC) Power



