The software for CT scanners comes with advanced image processing and analysis functions to generate High-resolution 3D images.
Benefits of X-ray CT system
- Observation from multiple directions
- Non-contact measurement
- Distance measurement
- Volume measurent
- Rendering object properties
- Utilized for reverse engineering
- Contributing to product development
(speedy visualization of defects)
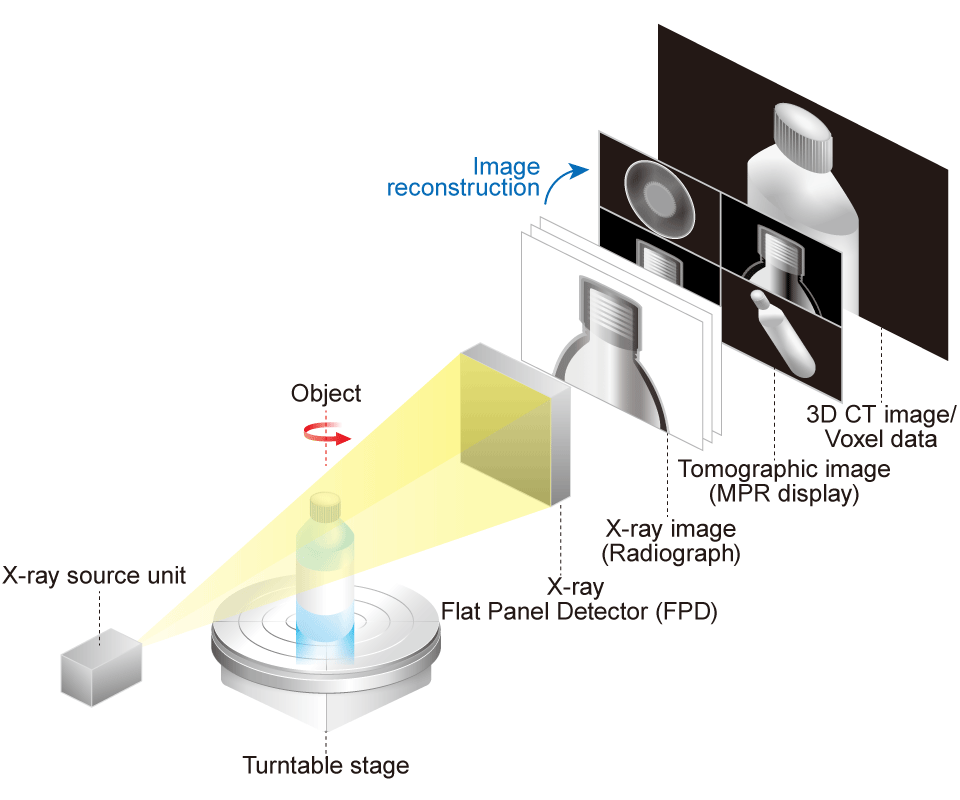
Computed Tomography Basics
Computed tomography (CT) is a type of nondestructive testing (NDT) technology that generates tomographic images using a computer. In X-ray CT, an X-ray generator and an X-ray detector (camera) are first used to capture the object's two-dimensional radiography (X-ray image). The object is rotated slightly in an industrial CT scan (micro CT), and X-ray images are taken from multiple directions. This type of imaging is called a cone-beam CT scan. Computer reconstruction software converts these sequential X-ray images into tomography (CT image). Furthermore, voxel data (3D CT image) can be obtained from the obtained tomography.
Normal scan vs Offset scan
In a Normal scan, if the width of the vision image of the sample is larger than the width of the X-ray camera, you need to shoot the sample repeatedly to obtain the tomographs. On the other hand, using offset scan, the center of the X-ray camera is shifted from the center of rotation of the sample for shooting, so a tomograph of a wide area at a time can be taken.


Models
| Function | -CTN | -CTDa | -CTM | -CTDaX | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scan mode | Normal scan | |||||
| Half scan | ||||||
| Offset scan | ||||||
| Reconstruction | Noise suppresion | |||||
| Metal artifact reduction | - | - | ||||
| Beam hardening reduction | - | - | ||||
| Ring artifact reduction | - | - | ||||
| Simple analysis | 2D | 2D cross-section surface display | ||||
| MPR image display | ||||||
| 3D | 3D tomographic image | - | ||||
| Volume rendering | - | |||||
| Measurement | Dimension (distance) measurement | |||||
| Angle measurement | - | - | ||||
| 2D/3D internal diameter measurement | - | - | ||||
| 3D fitting | - | - | ||||
| 3D particle analysis | - | - | ||||
| 3D drawing | - | - | ||||
| Saving in DICOM format | - | - | ||||
| 3D CT Image analysis software |
ROI visualization | Visualization | - | |||
| Creating and editing of ROI | - | - | ||||
| Volume/Surface area measurement | - | - | ||||
| Standard functions | Gray-scale value analysis | - | - | - | ||
| Data quality analysis | - | - | - | |||
| Arbitrary object separation | - | - | - | |||
| Reading | STL | - | ||||
| Point cloud | - | - | - | |||
| CT scan image | - | |||||
| VGL | - | |||||
| VGARCHIVE | - | - | ||||
| MVGL | - | - | ||||
| STEP/IGES (standard function) | - | - | - | |||
| Integrated mesh | - | - | - | |||
| Writing | Saved images | |||||
| 2D tomograhic movie | - | |||||
| Analysis report | - | - | ||||
| Images (of raw, ImageStack, etc.) | - | - | ||||
| Q-DAS file | - | - | ||||
| CAD (.stp) 3D movie | - | - | - | |||
| 3D movie | - | |||||
| Convert and Export | STL conversion | - | - | - | ||
| Surface mesh (STL) conversion | - | - | - | |||
| Volume mesh (tetrahedron) | - | - | - | |||
| Reverse engineering (CAD conversion) | - | - | - | |||
| Others | CAE collaboration | - | - | - | ||
| Merging filters/ images |
Advanced image merging | - | - | - | ||
| Gauss/Application gauss | - | - | - | |||
| Median | - | - | - | |||
| FIB/SEM correction | - | - | - | |||
*precision CT9600 has the -CTDa feature as standard, and selectable -CTDaX as an option.
RECONSTRUCTION
The image reconstruction process involves a computer generating cross-sectional images from the projection data collected by the CT scanner. This results in false and unwanted features in the image, called artifacts, which can be mitigated by software options.
Ring Artifact Reduction
Ring artifact reduction reduces concentric ring noise that occurs in tomographic images through a filtering process.
- -CTN
- -CTDa
- -CTM
- -CTDaX


Metal Artifact Reduction
The function reduces metal artifacts in the captured tomographic images.
It provides tomographic images with reduced metal artifacts for structural image analysis and internal observation.
- -CTN
- -CTDa
- -CTM
- -CTDaX


2D IMAGE

Here is an observation example of a capacitor (size approximately 0.24 inches (6 mm) in diameter, 0.39 inches (10 mm) in height.
- -CTN
- -CTDa
- -CTM
- -CTDaX
Arbitrary Tomographic Images
Ring artifact reduction reduces concentric ring noise that occurs in tomographic images through a filtering process.

Multi Planar Reconstructions (MPR)
Displays tomographic images of the 3D volume data from three directions.

3D IMAGE
- -CTN
- -CTDa
- -CTM
- -CTDaX
3D Arbitrary Tomographic Images
Visualizes volume-rendered 3D tomographic images.

Volume Rendering
Displays images that are generated from voxel data with all XYZ information. By changing the viewpoint, images from all directions can be displayed.

ANALYSIS FUNCTION
Dimension Measurement
Measures dimensions between specified points on a 2D image. The measurement results are reflected in a 3D image. (-CTN option is only 2D images.)
- -CTN
- -CTDa
- -CTM
- -CTDaX


Shortest Distance Measurement
Measures the shortest (or longest) distance on a 2D image. The distance is automatically measured by mouse dragging, and the dimensions display the dimensions of the shortest and longest parts. The measurement results are reflected in a 3D image.
- -CTN
- -CTDa
- -CTM
- -CTDaX


Volume/Surface Area Measurement
Measures the volume or surface area of a read 3D image.
- -CTN
- -CTDa
- -CTM
- -CTDaX

Arbitrary Object Separation
Arbitrarily extracts some part of an image to color or separate it.
- -CTN
- -CTDa
- -CTM
- -CTDaX

CAD Data Output
CAD data can be output in the STL file format, which represents the surface geometry of a 3D model as triangular polygons.
- -CTN
- -CTDa
- -CTM
- -CTDaX

Additional Analytical Functions (*-CTDax option required)
- -CTN
- -CTDa
- -CTM
- -CTDaX
| Reconstruction and quality analysis of image data |
|
|---|---|
| Surface determination |
|
| CAD import |
|
| GD&T |
|
| Reverse engineering |
|
| Material analysis |
|
| Volume mesh and simulation |
|
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T)
Using 3D display analysis data, you can check areas of sample structure, foreign matters, or shrinkage cavities in molding that cannot be measured by contact-type instruments. In addition, the function visualizes deviations and defect locations, facilitating sample inspection. It is suited for mold designs and inspections of shrinkage cavities in casting.
Comparison of design and CT data
By comparing CT data (actual measurements) with CAD data (design values), differences in shape can be visualized. Different colors can identify deviations.


Wall thickness analysis
Visualization of wall thickness analysis using CAD data and CT data is available. It is also available for errors in design values. The errors can be identified by color.

Wall thickness analysis (2D-display)
Three-dimensional images are used for the wall thickness measurement.

Material Analysis
Defect analysis
The defect analysis is used for detecting accurate location and size of defects in samples. It can also calculate the percentage of defects to the sample volume. It is available in the following categories.
- Scale (circumscribed sphere)/Volume
- Surface area
- Position XYZ
- Self - Sphericity
- Spacing (distance between defects)
- Projected size XYZ


Datasheets
If you are unable to download a file
Please try the following solution.
- Please press Ctrl+F5 to clear the cache of your web browser and try again.
- Please restart your web browser and log in again to try again.
- Please change your web browser to another browser and try again.
- Restart the computer and try again.
- Please try again on a different computer.
Login Required
-

Micro View X-Ray CT System Guide
Date: 2024-12-26 Rev.07
PDF (9,615 KB)
Information on related articles in Technical Knowledge
Similar products
-
New

precision µB4500
- X-ray tube voltage
- 90kV
- X-ray power
- 13.5W
Benchtop X-Ray CT Scanner -
New

precision CT9600
- X-ray tube voltage
- 130kV
- X-ray power
- 40W
X-ray Micro-CT Scanner -

µRay8700/µRay8760
- X-ray tube voltage
- 130V
- X-ray power
- 40W
X-ray Inspection System with optional CT functionHigh Penetrating Power X-ray Inspection System
-
New

precision μX8600
- X-ray tube voltage
- 130kV
- X-ray power
- 40W
Microfocus X-Ray Inspection SystemTop and Oblique Angle View