A bipolar power supply is a unit capable of producing both positive and negative voltage outputs. This article explores bipolar power supplies as four-quadrant power supplies that function as both a source (power supply) and a sink (load) in positive and negative polarities. It also discusses testing electrical components-an increasingly common application-with practical examples.
Whether you want to understand the basics of bipolar power supplies or plan to implement them in your work, this comprehensive guide provides valuable insights.

Basics of Bipolar Power Supplies
What is a Bipolar Power Supply?
In everyday life, we receive electricity from power companies through wall outlets. However, this utility power has certain limitations: it is alternating current (AC) at either 50Hz or 60Hz, with fixed voltages of 100V or 200V. Additionally, this power can contain unwanted noise, such as momentary voltage drops. For operating and testing various electronic devices, clean, stable power supplies capable of providing different DC voltage levels are required. This is where power supply units come into play.
A bipolar power supply, also known as a bipolar amplifier or power amplifier, is a versatile power supply device. What makes it particularly powerful is its ability to function as both a DC and AC power source while also acting as an electronic load. It is essentially an all-in-one power supply solution that combines the functionality of multiple power supply devices. One of its key features is its ability to operate in all four quadrants, meaning it can handle any combination of current and voltage directions.
Key Features of Bipolar Power Supplies
- Advantages: These units excel at high-speed operation, making them ideal for conducting power fluctuation tests that require rapid response times.
- Disadvantages: The main drawback is their cost. Bipolar power supplies are significantly more expensive than conventional power supply units, so careful consideration of the required functionality is essential when evaluating their use for specific applications.
Basic Structure
A key distinguishing feature of bipolar power supplies is their ability to generate both positive and negative voltages using two separate internal power systems.
The overall architecture consists of three main components: the output circuit, the protection circuit, and the cooling mechanism.
Output Circuit
The output circuit is the core component responsible for generating and delivering the required electrical power. This circuit performs several critical functions: it converts incoming AC power from wall outlets into the desired form, be it DC or a specific frequency or voltage. In addition, it filters out noise in the utility power and stabilizes current fluctuations caused by connected devices, ensuring consistent power delivery.
Most bipolar power supplies use either linear or switching regulators in their output circuits to perform these functions.
Protection Circuit
Bipolar power supplies incorporate protection circuits to guard against overvoltage, overcurrent, and short circuits. These protective features are essential because bipolar power supplies often handle high voltages and currents and are frequently used for testing various electronic devices that may exhibit unexpected behavior. The protection circuits act as critical safety measures, preventing damage to connected equipment and reducing the risk of fire in case of malfunction.
Cooling Mechanism
The process of voltage conversion and frequency modification in the output circuit generates heat. Excessive heating of the power supply can damage the unit and create unsafe operating conditions. To address this thermal challenge, bipolar power supplies use essential cooling mechanisms, such as forced cooling with fans and heat dissipation through heat sinks. These thermal management systems are crucial for maintaining the safe and reliable operation of the power supply.
Voltage Generation Methods
Bipolar power supplies use either linear regulators or switching regulators to generate the desired voltage output.
Linear Power Supply Method
The linear power supply method uses internal transistors to reduce voltage levels. This method only allows for voltage step-down operations, meaning it can only produce output voltages lower than the input voltage; it cannot boost voltage levels or create inverse voltages. While this method generates more heat and operates at lower efficiency compared to switching power supplies, it offers significant advantages. The linear method provides highly stable output with minimal noise, making it ideal for precision testing applications. Additionally, linear power supplies tend to be more cost-effective than their switching counterparts due to their simpler design and lower component costs.
Switching Power Supply Method
The switching power supply method regulates voltage through high-speed transistor switching operations. Unlike linear power supplies, this method offers greater versatility, capable of not only reducing voltage but also boosting and inverting it. This makes switching power supplies essential for applications that require voltages higher than standard 100V or 200V levels.
Due to their superior efficiency and ability to handle high power outputs, switching power supplies have become the predominant choice for bipolar power supply designs. However, this method does have one notable drawback: the switching operations inherently generate more electrical noise than linear power supplies.
Two-Quadrant and Four-Quadrant Operation
Power supply outputs are classified into four quadrants based on voltage and current polarity (+/−). Traditional DC power supplies, known as unipolar power supplies, operate only in the first quadrant (positive voltage and current) and the third quadrant (negative voltage and current). In contrast, bipolar power supplies can operate across all four quadrants, enabling both two-quadrant and four-quadrant operations.
Two-Quadrant Operation
In two-quadrant operation, the current flows in a single direction, while the power supply can switch between positive and negative output voltages. This allows operation across the first and fourth quadrants simultaneously. This capability is particularly useful for applications that require straightforward positive and negative voltage supply.
Four-Quadrant Operation
The distinguishing feature of bipolar power supplies is their ability to control both output voltage and current direction. Unlike conventional power supplies, they can handle current flow from the load back to the power supply. This full four-quadrant operation encompasses all quadrants, from the first through the fourth.
This capability is essential for applications such as evaluating motor reverse rotation or energy regeneration systems, where energy flows back from the load to the power supply. Four-quadrant operation is designed for applications that require more sophisticated control compared to two-quadrant operation.
Types of Bipolar Power Supplies
Bipolar power supplies come in several varieties. Here are four main types:
Bipolar Power Supplies with Built-in Signal Sources
These power supplies feature integrated signal generators capable of producing various waveforms. They are particularly valuable for applications that require high-speed, high-level signals, such as ultrasonic motor drives and display testing. This integrated design eliminates the need for external signal sources, allowing for comprehensive testing and evaluation using a single unit.
Bipolar Amplifiers for External Signal Amplification
These devices function as voltage amplifiers for external signals. For instance, they can take an input of ±10V and amplify it to ±10kV. Due to these amplification requirements, these units exclusively use switching power supply technology, as linear power supplies cannot achieve such amplification.
High-Voltage Amplifiers for Rapid Signal Processing
These specialized amplifiers are designed to handle high-voltage signals with rapid response times. The key parameter here is the slew rate-the rate of voltage change over time. High slew rates are essential for maintaining signal integrity when dealing with high-voltage signals, as lower rates can result in signal degradation and compromised response times. These units incorporate dedicated high-voltage amplifier modules to ensure optimal response characteristics.
Power Supplies for Piezo Drivers and Electrostatic Chucks
A specific category of bipolar power supplies is designed for piezo drivers and electrostatic chucks. These units excel at providing rapid responses to complex signal patterns, making them ideal for these specialized applications.
Applications of Bipolar Power Supplies
Bipolar power supplies serve diverse applications in both product evaluation and equipment power supply roles. Here are some key applications:
Battery-Powered Device Evaluation
When testing battery-powered devices, bipolar power supplies can accurately simulate battery behavior. They can reproduce various characteristics of battery operation, including voltage decay over time, allowing for comprehensive testing of battery-dependent devices.
Coil and Transformer Testing
Bipolar power supplies play a crucial role in testing coils and transformers by reproducing various electrical input signals needed to thoroughly evaluate these components.
Capacitive Load Testing
For testing capacitors and other capacitive loads, bipolar power supplies provide the flexibility needed for comprehensive evaluations. Since capacitance can vary with frequency and voltage, these power supplies enable testing across different frequencies and voltage levels.
Solar Cell Equipment Testing
With the growing emphasis on environmental sustainability, solar cell technology has seen increasing demand. Testing solar cell equipment often requires high-voltage capability, making bipolar power supplies essential for these evaluations.
Motor Testing
Motors come in various sizes and specifications, requiring versatile testing capabilities. Bipolar power supplies can apply different voltage and current loads to motors and evaluate regenerative current during reverse rotation.
Surface Treatment Applications
Industrial surface treatment processes, such as high-frequency hardening, require high-voltage AC current. Bipolar power supplies provide the necessary power characteristics for these specialized applications.
Testing Automotive Electrical Systems
One of the fastest-growing applications for bipolar power supplies is testing automotive electrical components. This growth stems from the increasing adoption of electric vehicles and the integration of numerous safety systems, both of which have led to a surge in automotive electronic components. The confined space within vehicles now houses various electrical components, creating multiple power supply patterns and resulting in highly complex voltage fluctuation patterns. Furthermore, automotive electrical components must meet various safety standards, requiring evaluation under these complex power conditions. This is precisely why bipolar power supplies have become essential. While there are numerous industry standards, automotive manufacturers also establish their own specifications and require their electrical component suppliers to conduct testing and deliver products that meet these requirements.
Standards
The following standards apply to automotive electrical components:
| ISO16750-2 | Environmental conditions and testing specifications for electrical and electronic equipment in road vehicles |
|---|---|
| ISO7637 | Testing standards for electrical disturbance in road vehicles |
| ISO10605 | Standard protocols for electrostatic discharge testing |
| AEC-Q100/Q200 | Automotive industry-specific reliability testing standards for electronic components |
| ISO 26262 | Comprehensive functional safety standards for automotive systems |
| UN/ECE R10 | Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards for vehicles |
|
SAE J1113 Series & ISO 11452 Series |
EMC testing standards for automotive electrical equipment |
| LV124 | German automotive manufacturers' testing specifications for vehicle electrical components |
| LV148 | |
| LV123 | Testing standards for high-voltage automotive electrical components using bi-directional power supplies |
Testing Requirements
The aforementioned standards encompass a variety of tests, including rapid voltage fluctuation and voltage ripple testing. Additional requirements include load interruption testing, voltage limitation evaluation, and offset voltage testing. Standard power supplies often struggle to perform these tests effectively, particularly when testing components with high reactance loads. Bipolar power supplies offer the flexibility needed to conduct these sophisticated evaluations.
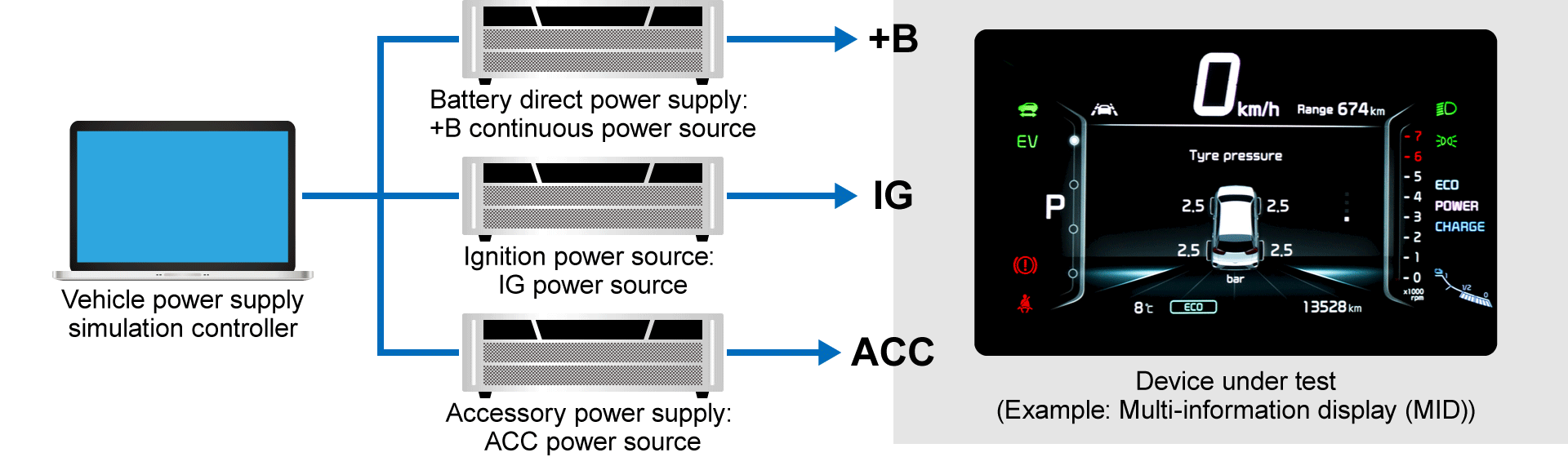
Testing Navigation Systems with Bipolar Power Supplies
Vehicle navigation systems operate on power from the car's battery and related power systems. As previously discussed, multiple electrical components share this power source, with each component operating in complex patterns that create intricate power fluctuations. Bipolar power supplies are used to verify that navigation systems function properly under these conditions and do not generate electrical interference that could affect other vehicle systems.
A typical test system configuration is outlined below.
Key Factors in Selecting Bipolar Power Supplies
A wide range of bipolar power supplies is available on the market. To select the most suitable unit for your application, several critical factors must be considered.
Voltage and Current Output Range
One of the most crucial factors in selecting a bipolar power supply is its voltage and current output range.
For instance, in Matsusada Precision's product line, output voltage ranges vary significantly-from units offering ±20V-60V to those providing ±0.5kV-1kV. The selection should align precisely with your application's specific requirements.
Response Speed Capabilities
Different applications demand different response speeds. Some applications, such as high-voltage signal testing, require rapid response times, while others, like battery aging simulation tests, can operate with lower response rates. For example, Matsusada Precision offers units with response speeds ranging from DC to 10kHz, and others extending from DC to 1,000kHz.
Thermal Management
Depending on their output voltage and load requirements, some applications can generate significant heat in power supply units. In these cases, it's essential to select bipolar power supplies with robust thermal management systems.
Introduction to Matsusada Precision's Bipolar Power Supplies
Matsusada Precision offers several types of bipolar power supplies for different applications:
Built-in Signal Generator Type Bipolar Power Supply
This model features an integrated signal generator and can serve as a battery simulator for testing battery-powered devices. It can also be used for testing inductive loads such as coils and transformers.

External Input Type Bipolar Power Supply
This model accepts external signal inputs and is suitable for testing capacitive loads like capacitors or for use as a power conditioning system.

Function Generator (External Signal Source)
Function generators connect to external input type bipolar power supplies to generate custom waveforms and test signals.




