The X-ray comparison shows images of four different batteries arranged from left to right: an AA-size manganese battery, an alkaline battery, a nickel-metal hydride (rechargeable) battery, and an 18650-size lithium-ion battery (rechargeable, not commercially available).




| Battery Types | Structural Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Manganese battery | The key structural difference between manganese and alkaline batteries is visible in their current collectors. In the X-ray image, the materials surrounding the current collector (manganese and zinc) show varying darkness, with zinc appearing darker due to its higher atomic number. |
| Alkaline battery | |
| Nickel-metal hydride battery | This battery features an insulating tube wrapped around its negative electrode. Due to its nickel composition, the negative electrode appears darker in X-ray images at the same exposure level. |
| Lithium-ion battery | The internal structure consists of alternating layers of cathode plates, anode plates, and separators, all contained within an outer case. |
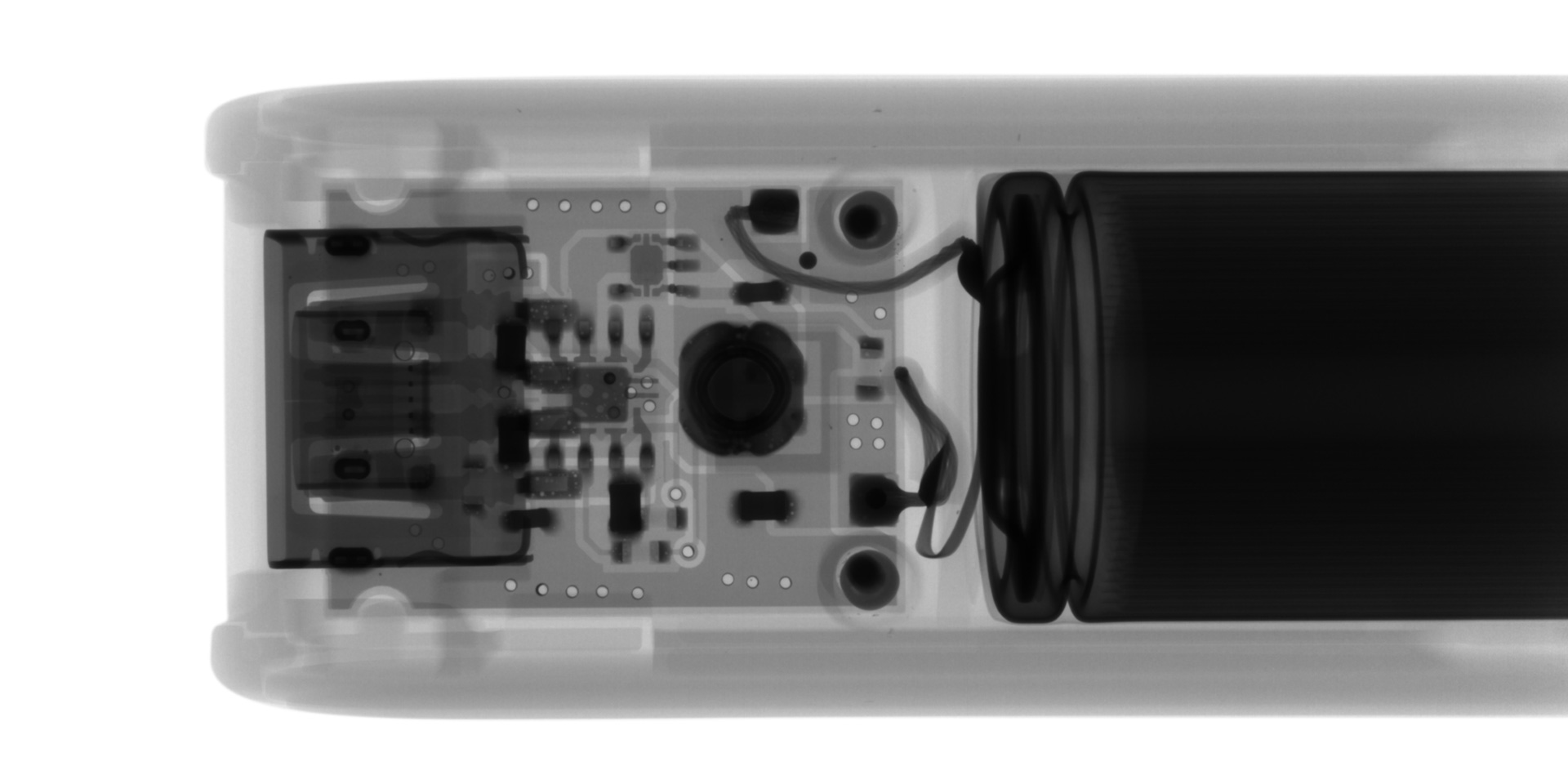
The X-ray image of the novelty mobile battery charger reveals its internal components from left to right: the USB terminal, circuit board, and socket. The detailed scan clearly shows the wiring connections between the circuit board and socket, as well as the circuit board's through holes and internal wiring patterns.
X-ray system requirements
| Focal spot | Microfocus |
|---|---|
| X-ray tube voltage | 130 kV |
Recommended products
Information on related articles in Technical Knowledge
- The Right Way to Choose appropriate X-ray Inspection System
- Principles of Radiography
- How to use X-ray Inspection System safely
- What is Microfocus X-ray? (Basic Knowledge)
- Computed Tomography (CT) Basic and Principle
- Non-Destructive Testing: Types and Applications
- What are X-rays? (Basic Knowledge)
- How to Take a Computed Tomography? - X-Ray NDT series (1) -
- How to View X-ray CT Images - X-ray Non-Destructive Inspection series (2) -
- X-ray Image Processing and Automated Inspection - X-ray Non-Destructive Inspection series (3) -
- Types of X-ray tubes and high-voltage power supplies
- What is the difference between Radioactivity, Radiation, and Radioactive Materials?
- Radiation Effects on the Human body and the safety of X-ray equipment






