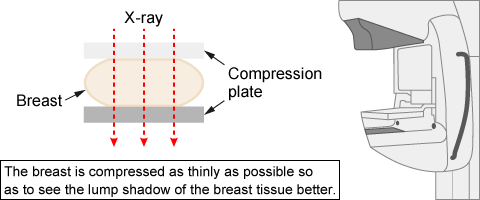
Mammography is a specialized medical imaging technique using low-dose X-rays to screen for and diagnose breast cancer. The procedure involves compressing the breast between two plates and capturing images using an X-ray system specifically engineered for soft tissue imaging.
X-rays are attenuated differently depending on tissue density; they penetrate low-density materials easily but are absorbed by high-density materials. This contrast allows for clear imaging of internal breast structures. A key advantage of mammography is its ability to image the entire breast and detect microcalcifications--tiny calcium deposits that can be an early indicator of cancer--which are often difficult to detect with ultrasonography.
X-ray Generation and Power Supply Requirements
In a mammography system, X-rays are produced when electrons, emitted by a heated filament (cathode), are accelerated toward a metal target (anode) such as tungsten or molybdenum. This process requires precise power management: a high-voltage power supply to accelerate the electrons and a filament power supply to heat the cathode. These power supplies are critical for ensuring stable X-ray output and high-resolution imaging.
Matsusada Precision offers a wide range of high-voltage power supplies optimized for X-ray tubes, including models with integrated floating filament supplies for compact and reliable system integration.
- Related words:
-
- Breast Cancer
- X-Ray
Recommended products
We offer a variety of high-voltage power supplies for X-ray tubes, including models with integrated current sources for filament heating.
Information on related articles in Technical Knowledge
- Principles of Radiography
- Safe Operation of X-ray Inspection Systems
- What are X-rays? (Basic Knowledge)
- What is the difference between Radioactivity, Radiation, and Radioactive Materials?
- Understanding Radiation: Effects on the Body and X-ray Safety
- Types of X-ray Tubes and High-voltage Power Supplies







