What is a high-voltage power supply?
A high-voltage power supply is a voltage conversion circuit that boosts a low input voltage potential to a higher voltage potential for output. There are many definitions of high voltage. At Matsusada Precision, we classify power supplies that output 1000 V or more as high-voltage power supplies. In general, a high-voltage power supply refers to a power supply that outputs a DC high voltage.
Where are high-voltage power supplies used?
In research and development, higher voltages are needed to operate equipment under different conditions and create a special environment for testing. In particular, mass spectrometry and electron microscope scientific instrumentation, X-ray inspection equipment, optical communications, and space science experiments require strong electric fields to control and detect electrons in the equipment. High voltage is essential to generate a strong electric field. If high voltage is required in this way, use a high-voltage power supply.
High voltage generation method
The method most often used for generating high voltages is the Cockcroft-Walton circuit. It consists of a multi-stage combination of capacitors and diodes, as shown in the following circuit diagram. Increasing the number of stages in the Cockcroft-Walton circuit increases the voltage to the desired level.

The Cockcroft Walton circuit is also called a CW circuit, Cockcroft Walton generator, or Cockcroft Walton multiplier.
Type of high-voltage power supply
Various types of high-voltage power supplies exist. Each of the following items can be classified into different types.
- Installation method: PCB mount, chassis mount, benchtop, rack mount
-
High-voltage power supplies can be classified into printed circuit board (PCB)-mounted, chassis-mounted (module), bench-top, and rack-mounted types, depending on the shape of the power supply.
- Output type: positive polarity output, negative polarity output, positive/negative switchable output, bipolar output, pulse output
-
The high voltage output can be classified into positive polarity output type, negative polarity output type, positive/negative polarity switching type, bipolar output type, and pulse output type. In many high-voltage applications, the polarity of the output is meaningful, so care must be taken to avoid polarity errors.
- Input power: AC input (AC-HVDC), DC input (DC-HVDC)
-
High-voltage power supplies can be classified into AC input type and DC input type according to the input power of the high-voltage power supply. The AC input type is a high-voltage power supply that can output higher voltage or high power output. Most benchtop and rackmount models are AC input types. Most high-voltage power supply modules are DC input type low-voltage DC to high-voltage DC converters (DC-HVDC).
- Control method: Proportional, analog control, digital control
-
The following three types can be classified by the method of controlling the output voltage. The proportional type controls the output voltage according to the voltage of the input DC power supply. Outputs a high voltage proportional to the input voltage. Analog control is controlled by inputting the set voltage according to the output voltage to the analog control terminal. For models with a reference voltage pin, the output voltage can also be controlled by a variable resistor. Digital control controls output via digital signals such as LAN, USB, RS-232C, or RS-485. Digital control provides remote and safe control. In addition, long-distance control and isolated control can be achieved with optical fiber.
Matsusada Precision's high-voltage power supplies
High-voltage power supplies are essential in many industries and sectors, including electronics, semiconductor, science, analytical, medical, healthcare, aerospace, environmental, industrial, manufacturing and research facilities. High-voltage applications are devices that require action by electric fields and electrons due to high voltage. Familiar examples of high-voltage power supplies include hospital X-ray machines, semiconductors used in smartphones and electronic devices, and display manufacturing equipment.
We at Matsusada Precision believe that understanding the different types of high-voltage power supplies available is key to selecting the right one for any given application. The term "high-voltage power supply" refers to a DC power supply that outputs high voltage.
At Matsusada Precision, we classify programmable power supplies with meters that can output voltages of 1000 V or more and embedded power supply modules that can output voltages of several hundred volts or more as high-voltage power supplies.
Whether they are classified as high voltage or simply DC depends on each company's product line and voltage.
OUR PRODUCTSInstallation Method
PCB mount (on-board) type high-voltage power supply
Printed circuit board (PCB) mounting type high-voltage power supply modules are input and output pins through-hole mounting electro components. This on-board module converts low-voltage DC to high-voltage DC (DC to HVDC) and does not come with an indicator or controller. This high-voltage power supply requires a DC power supply such as 5 V or 12 V for input and a control circuit for output voltage control. When designing a Printed circuit board, ensure that there is sufficient creepage distance between the high voltage output and ground or other wires. Careful design should be taken to prevent creepage discharge and migration. There are products with a resin body and products with a metal body. The metal module is electromagnetically shielded and has excellent heat dissipation.
The supply range of our on-board high voltage power supply is from 50V to 10kV voltage and 0.1W to 30W power.
Chassis-mount high-voltage power supply modules
Chassis-mount type high-voltage power supply modules are high-voltage power supplies with no indicator or control circuitry, ideal for embedded applications in customer equipment. Most high-voltage power supply modules output via a high-voltage cable coming directly from the module.
The supply range of our chassis-mount high-voltage power supplies is from 0.3kvV to 50kV voltage and 1W to 1.2kW power.
Benchtop High Voltage Power Supplies
Bench-top high-voltage power supplies are compact, high-voltage power supplies that can be used immediately by simply connecting them to a commercial AC power source. The indicator and voltage adjustment volume makes it easy to set the output voltage. In addition, the high-voltage output uses a high-voltage connector for easy and safe connection to the load.
Our bench-top high voltage power supplies range from 1kV to 30kV voltage and 3W to 200W power.
Rackmount High Voltage Power Supplies
Rack-mount high-voltage power supplies are power supplies that are housed in a 19-inch wide rack cabinet. This category includes ultra-high voltage and high power high voltage power supplies. It is ideal for building Automatic test equipment or automated test equipment (ATE) and manufacturing process equipment in combination with other measuring instruments. Models are available that allow digital control from LAN or other means as well as an analog remote control.
The supply range of our rack-mount high voltage power supplies is from 1kV to 200kV voltage and 30W to 13000W power.
Output Type
When it comes to high-voltage power supplies, understanding the different polarities available is essential. You will commonly find power supplies with positive-polarity output, negative-polarity output, or the capability to switch between both.
It's imperative to carefully consider these options and select a power supply that matches the polarity requirements of your application. It's imperative to carefully consider these options and select a power supply that matches the polarity requirements of your application. High-voltage DC power supplies are polarity specific, meaning that the output voltage of a high-voltage power supply is above or below ground, depending on its output polarity. The positive high-voltage power supply provides the positive voltage and positive current. On the other hand, the negative high-voltage power supply provides a negative voltage and negative (sinking) current. This corresponds to the third quadrant of the four-quadrant diagram of the voltage and current vectors. The negative power supply does not consume power.
High voltage applications are inherently dangerous, and using a power supply with the incorrect polarity could result in damage, injury, or worse. Therefore, it's essential to pay close attention to polarity when purchasing a high-voltage power supply.
Positive Polarity Output
The importance of choosing the right polarity for a device cannot be emphasized enough. It all boils down to the structure and application. Whether you need a positive or negative terminal will depend on the device's requirements. This nuance is especially crucial for silicon avalanche photodiodes (Si-APDs), which will need a high-voltage positive terminal to operate optimally.
In conclusion, it's essential to discern the device's unique needs before choosing the appropriate terminal and providing the ideal operating conditions.
Positive or Negative polarity outputs, Nearly all of our high-voltage power supplies are selectable.
Negative Polarity Output
For certain applications, like radiation detection devices, a high-voltage power supply with a negative polarity is necessary. Luckily, the Negative Polarity Output type fits the bill perfectly. This specialized type of output is specifically meant for situations where electrons are emitted from the negative side at a high voltage.
Devices like PMTs, SDDs, and Geiger counters require a great deal of precision and accuracy in their design, and this type of output helps to ensure that their power supply needs are met. Whether you're conducting scientific research or building your own radiation detection device, the Negative Polarity Output type is an essential piece of the puzzle.
Positive or Negative polarity outputs, Nearly all of our high-voltage power supplies are selectable.
Positive/Negative Reversible Output
The concept of reversing polarity may sound like a foreign idea to the average person, yet it plays a critical role in scientific experimentation. The technique involves altering the electric charge of a sample, allowing scientists to study the impact of different polarities.
This approach can be particularly useful in analyzing how certain elements react to specific electrical charges. Additionally, polar reversal is often employed in applications where ions in mass spectrometers are manipulated. By flipping between cation and anion samples, researchers gain valuable insights into the properties of these charged particles.
Ultimately, the use of reversing polarity highlights how cutting-edge scientific methods are continually reshaping our understanding of the world around us.
Reversible polarity output type Matsusada Precision's high voltage power supplies
Bipolar output type high-voltage amplifiers
Bipolar output type high voltage power supplies are called high voltage amplifiers. The high-voltage amplifier outputs a high voltage that amplifies the waveform of the input signal to a high magnification. High-voltage amplifiers are also high-speed, high-voltage amplifiers with fast slew rates because they require outputs with large amplitude. For more information on high-voltage amplifiers, see Application: "High-Voltage Amplifiers".
Our high voltage amplifiers supply ranges from 0.3kV to 40kV voltage and 3W to 1200W power with slew rates up to 1200V/us.
Pulse Output Type High Voltage Power Supply
High-voltage pulse power supplies are power supplies that can output high-voltage pulses at high speed.
Our high-voltage pulse power supply range is up to 10 kV in voltage.
Input Power
AC Input (AC-HVDC)
When it comes to choosing a power supply, the AC input type is a popular choice for those looking for high voltage and power output. This type of power supply is capable of meeting the power demands of many electronic devices. If you're in the market for a bench-top or rack-mount model, chances are you'll come across many AC input types.
These models are dependable and often offer additional functionality that makes them an excellent choice for those who need to meet higher power output requirements. Most AC input types have a meter and volume and are ready to use immediately after purchase. In addition, the high-voltage output is connectorized so it can be detached.
Matsusada Precision's rackmount and benchtop high voltage power supplies are AC input types. Some of our high-power high-voltage power supply modules are also AC input types.
DC Input (DC-HVDC)
When it comes to powering high-voltage applications, DC to high-voltage DC converters, also known as High voltage DC-DC converters or DC-HVDCs, are the way to go. These ingenious devices have revolutionized the way we transmit and distribute electrical power, providing us with compact, highly efficient solutions for converting low-voltage DC power to high-voltage DC power.
DC-HVDC (so-called high-voltage modular power supplies) are used in analyzers, medical testing equipment, radiation measuring instruments, electron microscopes, and semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
All Matsusada Precision on-board types and most of our high voltage modules have DC input type high voltage power supplies.
Control Method
Proportional
This type of control utilizes the input voltage of the DC power supply to determine the output voltage. In essence, it's a high-voltage response that's directly proportional to the input. This means that as the input voltage rises, so too does the output voltage. It's a seamless and precise process that ensures that your electrical applications receive the exact amount of power they need to operate correctly.
This is a type of DC-HVDC control method. Generally, the input-output proportional method is simple and inexpensive. It is more compact with fewer wires and pins to control.
Introducing Matsusada Precision's proportional-type high-voltage power supplies. Naturally, only DC input-type modules are available.
Analog Control
The analog control system inputs a set voltage based on the output voltage to the analog control terminal. If your device has a reference voltage pin, you can even control the output voltage using a variable resistor.
This allows for a high degree of precision, ensuring that your device operates as efficiently and effectively as possible. Analog control is a feature found on most high-voltage power supplies, from non-proportional modules to rack-mounted units.
In addition to controlling output voltage, some power supplies can also control ON/OFF, current, and monitor output.
Analog control terminals are provided on most of Matsusada Precision's high-voltage power supplies.
Digital Control
Digital control allows for the utilization of digital signals, such as LAN, USB, RS-232C, or RS-485, to control the output of a device. With digital control, safety is not only ensured but remote control of devices is made possible. This means you can change the output level of a device from a distance.
Moreover, the advantage of fiber optics is that it provides more distant remote control and protection against electrical disturbances.
In other words, it reduces the risk of damage to peripheral equipment due to electrical discharges or short circuits.
Digital control is communicated by either a metal wire connection or an optical fiber connection, depending on the output voltage. Many of our rack mount and bench top high voltage power supplies support digital control. Note that direct digital control may be possible, or an interface adapter may be required.
Dedicated type high voltage power supply
Dedicated-type high-voltage power supplies are power supplies with application- and device-specific features and output ranges. Matsusada Precision introduces high voltage power supplies for electrostatic chucks, X-ray tubes, piezo element drives, PMTs, mass spectrometers, electron beams, and xenon lamps.
High Voltage Power Supplies for Electrostatic Chucks
Power supplies for electrostatic chucks are dedicated high-voltage power supplies for electrostatic chucks that secure semiconductor wafers. For more information on electrostatic chucks, see Application: "Electrostatic Chucks".
High-voltage power supply for X-ray tubes
The high-voltage power supply for X-ray tubes combines a high-voltage power supply for accelerating electrons and a low-voltage power supply for the filament. There are two types of high-voltage power supplies for X-ray tubes: anode-grounded and cathode-grounded. There is also a bipolar connection, in which the high-voltage power supply is connected to both poles. For more information on types of X-ray tubes and high-voltage power supplies, please refer to "Types of X-ray tubes and high-voltage power supplies" in the Technical Tips.
We also offer an X-ray generator module that includes an X-ray tube and a high-voltage power supply.
The supply range of our high voltage power supplies for X-ray tubes is from 30kV to 160kV voltage and 50W to 4000W power.
High-voltage power supply for driving piezoelectric elements
High-voltage power supplies for driving piezoelectric elements are called piezoelectric drivers. Used to drive piezo actuators or piezo precision stages.
For more information on piezo drivers, see "About Piezo Drivers" in the Tech tips.
High-voltage power supplies for photomultiplier tubes
High voltage power supplies for photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) are power supplies for PMTs used in detectors of analyzers, radiation measuring instruments, and medical equipment to detect weak light. Socketed and modular power supplies dedicated to PMT are available. To use a photomultiplier tube, in addition to a high-voltage power supply, a divider circuit corresponding to the number of dynode stages and a detection circuit to read out the signal are required.
For more information on photomultiplier tubes, see Application: "Photomultiplier Tubes: PMT".
High voltage power supply for mass spectrometry
High voltage power supplies for mass spectrometrys are low noise, highly stable, high-performance special power supplies that do not affect the accuracy of the analysis. There are various types of mass spectrometers. Among them, TOF-MASS requires multiple high-performance, high-voltage power supplies.
For more information on mass spectrometers, see Applications: "Mass Spectrometry".
High-voltage power supplies for electron beam applications
The high-voltage power supply for electron beams in electron microscopes combines a high-voltage power supply for acceleration, a power supply for filaments, and a power supply for electrodes such as wenelts, suppressors, and extractors. In addition to high-voltage power supplies, electron microscopes use DC power supplies for lenses, bipolar power supplies for scanning and axis correction, and PMT power supplies for detectors.
For more information on electron microscopy, see Applications: "Electron Microscope" and tech tips.
High voltage power supply for ion beam
The high-voltage power supplies for ion beams here are introduced for ion sources used in FIBs and other applications. For ion implantation, analyzers using ions and medical equipment, multiple DC power supplies as well as high-voltage power supplies for ion beams are used.
For more information on Ion Beam, see Applications: "Ion Beam" and tech tips.
High-voltage power supply for xenon flash lamps
The high-voltage power supply for xenon lamps is a dedicated high-voltage power supply for xenon flash lamps that combines the main high-voltage output with an output for triggering.
High-voltage power supply for electrophoresis
High Voltage Electrophoresis Power Supplies are built-in constant linear voltage-controlled power supplies that are used to separate molecules based on their electrophoretic mobility in an electrical field.
They are used for applications such as electroblotting, agarose gel electrophoresis, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and DNA sequencing. They are highly stable, and some manufacturers provide USB compatibility to monitor the progress of electrophoretic experiments.
Advantages of Using High Voltage Power Supplies
Efficiency
High-voltage power supplies are highly efficient and can convert the energy from the power source to the output with minimal loss. This is because they require less current to transmit the same amount of power, reducing power loss due to cable resistance and heating effects. This makes high voltage supplies economical, as less energy is wasted as heat, and more of it is used by the device.

High power density
High-voltage power supplies can provide high power in a small package compared to low-voltage power supplies. They can handle high-power processing and switching due to the high voltage they provide. This makes high-voltage supplies suitable for applications that require high power density and efficiency, such as medical equipment, industrial lasers, and semiconductors.

Stability
High-voltage power supplies offer better stability than low-voltage power supplies. They can maintain a constant voltage level despite fluctuations in the input voltage. This is because they have better regulation, reducing the ripple and noise that can affect the device's performance. Additionally, high-voltage supplies have a superior short circuit and overload protection mechanism compared to low-voltage supplies.
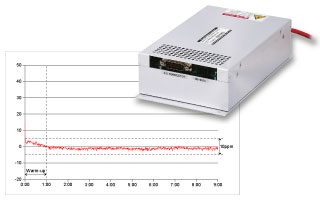
Safety
High-voltage power supplies are safer to use because they require less current to transmit the same amount of power. This reduces the risk of electrical shocks and makes it safer to use in sensitive environments like laboratories. Additionally, high-voltage supplies can switch off quickly in case of a fault, reducing the risk of damage to the device or the user.

Versatility
High-voltage power supplies are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications. They can provide different voltage levels depending on the device's requirements. They can also operate at different frequencies, making them suitable for different devices, including LEDs, motors, and sensors.

Matsusada Precision's High Voltage Power Supplies
Looking for the best possible power supply solution for your business? Look no further than Matsusada Precision's high-voltage power supplies! Our impressive selection of high-quality power supplies is expertly manufactured in Japan, utilizing years of experience and cutting-edge technology to offer unparalleled reliability and efficiency.

With low noise, high stability, and peak performance, Matsusada Precision's power supplies are the perfect choice for any business looking to take its equipment to the next level. Plus, with exceptionally fast delivery times, you'll be up and running in no time. Trust us to deliver the power you need to succeed!
Safe use of high-voltage power supply
CAUTION: High-voltage power supplies generate high voltages and can be harmful to the human body if used improperly. Refer to "Safety and Usage of High Voltage Power Supplies" for proper use.